Financial Accounting Online Tutor, Practice Problems & Exam Prep

That’s why you’re better off starting with double-entry bookkeeping, even if you don’t do much reporting beyond a standard profit and loss statement. While the accounting equation goes hand-in-hand with the balance sheet, it is also a fundamental aspect of the double-entry accounting system. Assets entail probable future economic benefits to the owner.
Assets
Since the accounting equation depicts a mathematical equality, it also follows that all debits must always equal all credits. In other words, a journal entry should have a minimum of at least one debit entry and one credit entry, and the total of those entries must be equal. Owner’s equity is the residual interest or amount that assets exceed liabilities.
Balance Sheet and Income Statement
In all financial statements, the balance sheet should always remain in balance. The accounting equation is a concise expression of the complex, expanded, and multi-item display of a balance sheet. This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends. The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry bookkeeping practice. Its applications in accountancy and economics are thus diverse.
Effects of Transactions on the Accounting Equation
- This observation tells us that accounting statements are important in investment and credit decisions, but they are not the sole source of information for making investment and credit decisions.
- These are fixed assets that are usually held for many years.
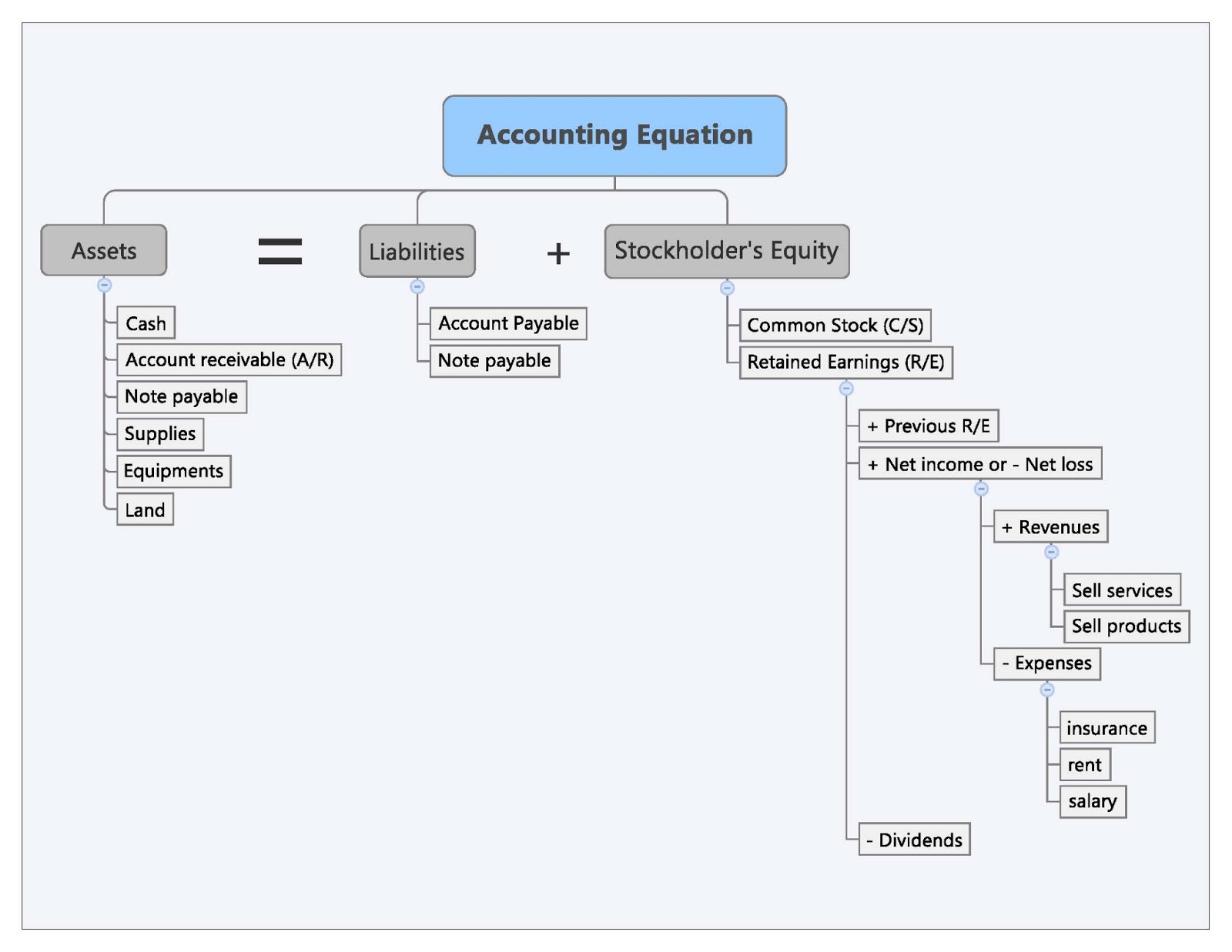
- The fundamental accounting equation, as mentioned earlier, states that total assets are equal to the sum of the total liabilities and total shareholders equity.
- So good examples of those are going to be things like land or machinery or if we buy a building, right?
- As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. Because it considers assets, liabilities, and equity (also known as shareholders’ equity or owner’s equity), this basic accounting equation is the basis of a business’s balance sheet. However, in simple terms, debits and credits are merely the two sides of the accounting equation.
The basic accounting equation at a glance
The business has paid $250 cash (asset) to repay some of the loan (liability) resulting in both the cash and loan liability reducing by $250. We will now consider an example with various transactions within a business to see how each has a dual aspect how invoice financing works and to demonstrate the cumulative effect on the accounting equation. In the case of a limited liability company, capital would be referred to as ‘Equity’. On the other side of the equation, a liability (i.e., accounts payable) is created.
What Is a Liability in the Accounting Equation?
The accounting equation will always balance because the dual aspect of accounting for income and expenses will result in equal increases or decreases to assets or liabilities. Accounting equation describes that the total value of assets of a business entity is always equal to its liabilities plus owner’s equity. This equation is the foundation of modern double entry system of accounting being used by small proprietors to large multinational corporations. Other names used for this equation are balance sheet equation and fundamental or basic accounting equation. One of the main financial statements (along with the balance sheet, the statement of cash flows, and the statement of stockholders’ equity). The income statement is also referred to as the profit and loss statement, P&L, statement of income, and the statement of operations.
After six months, Speakers, Inc. is growing rapidly and needs to find a new place of business. Ted decides it makes the most financial sense for Speakers, Inc. to buy a building. Since Speakers, Inc. doesn’t have $500,000 in cash to pay for a building, it must take out a loan. Speakers, Inc. purchases a $500,000 building by paying $100,000 in cash and taking out a $400,000 mortgage. This business transaction decreases assets by the $100,000 of cash disbursed, increases assets by the new $500,000 building, and increases liabilities by the new $400,000 mortgage. Although the balance sheet always balances out, the accounting equation can’t tell investors how well a company is performing.
Equity represents the portion of company assets that shareholders or partners own. In other words, the shareholders or partners own the remainder of assets once all of the liabilities are paid off. Receivables arise when a company provides a service or sells a product to someone on credit. For more insights into the accounting equation, consider enrolling in accounting courses or reading specialized literature.
11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site.
Like any mathematical equation, the accounting equation can be rearranged and expressed in terms of liabilities or owner’s equity instead of assets. That part of the accounting system which contains the balance sheet and income statement accounts used for recording transactions. If a company’s assets were hypothetically liquidated (i.e. the difference between assets and liabilities), the remaining value is the shareholders’ equity account. We know that every business holds some properties known as assets. The claims to the assets owned by a business entity are primarily divided into two types – the claims of creditors and the claims of owner of the business.
